Developing and Sustaining Agile Leaders, Teams, and Organizations
In Part One [insert link] I shared the inspiration for this three-part series. In a nutshell, this series is for anyone whose organization has made agility a top strategic priority. This includes, but is not limited to, companies that are adopting agile methodologies at the team level, are starting to scale agile across the enterprise (see Part Two of this series), or have more broadly understood that business agility is critical to staying competitive in a rapidly changing world. This final post is for you if your organization fits any of these categories, and you want to assure that your investment in business agility delivers the results you seek.
“Where Should We Start?”
The question above is the first one leaders ask after committing to being more agile. Of course, before we can answer that question, we must agree on what are we talking about when we talk about agility?
Broadly, I describe agility as your ability to respond effectively to the unexpected and unplanned and quickly turn challenges into opportunities.
This is not a dictionary definition but a performance statement. The leaders I work with don’t need to know what agility looks like on paper; they need to know what it looks like in action.
The goal of any agile initiative is not agility itself, but sustained performance through both stable and volatile conditions.
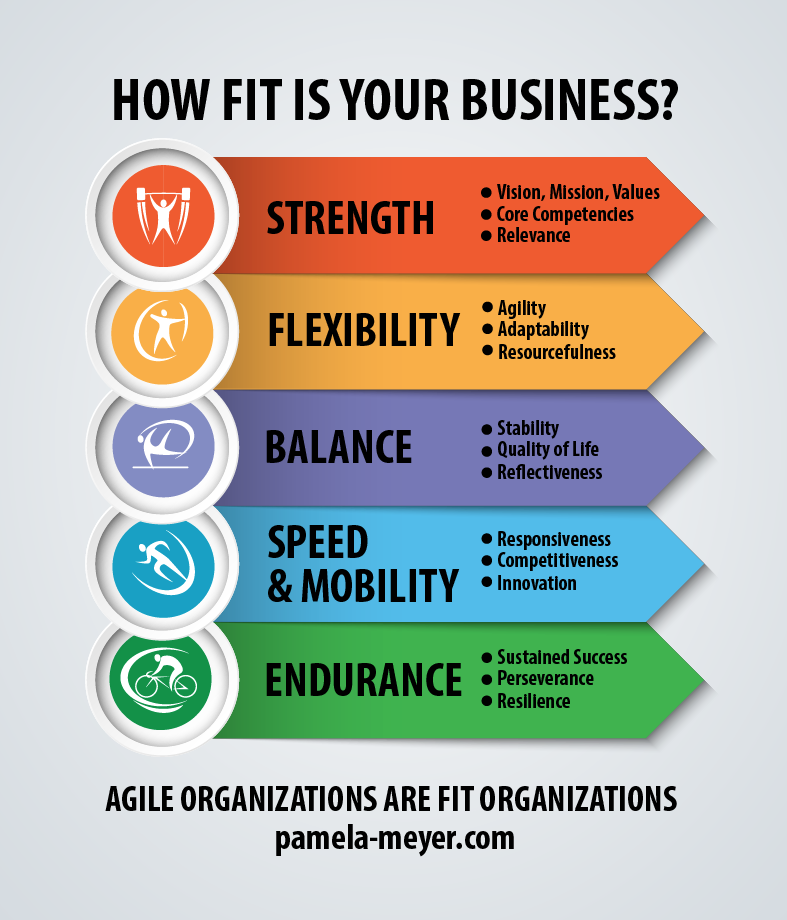
To consistently achieve this level of performance, the organizations I have researched and work with consistently attend to each of the six dynamics of the Agility Shift. To fully understand each dynamic and how to bring it to life in your organization, I direct you to my book, The Agility Shift: Creating Agile Leaders, Teams and Organizations, as well as my website for additional resources. Below is a brief introduction to each of the dynamics:

Relational Web: The network of skills, knowledge, talent, and resources that you need to be able to tap at a moment’s notice when things don’t go as planned or a new opportunity emerges.
Relevant: The ability to understand current trends, customer and workforce needs, and adapt to stay relevant to and competitive in the market.
Responsive: The ability to respond in a timely and effective way to unexpected and unplanned challenges and opportunities.
Resilient: The ability to quickly regroup when things don’t go as planned.
Resourceful: The ability to make optimal and innovative use of available resources.
Reflective: The ability to learn the lessons from experience and thoughtfully apply those lessons to new and emerging situations.
Agility and Agile methodologies are certainly not mutually exclusive. You don’t need to adopt a specific agile methodology to improve your leadership, team, or organizational agility. Yet, adopting an agile methodology without attending to the necessary mindset, culture, and practice shifts will not yield the hoped-for results, especially over the long haul.
Making the Mindset and Culture Shift So Agility Can Thrive
Now that we have a shared understanding of agility and the six dynamics necessary to sustain it, we must understand and make (and continue to make) the mindset and culture shift required to thrive in this radical (for many) new ways of working.
A recent joint global survey by Forbes Insights and the Scrum Alliance of 1,000 C-suite executives across industries that found 83% of respondents cite an agile mindset/flexibility as the most essential characteristic of today’s C-suite (2018).
At its core, an agile mindset and culture value learning and change over planning and control.
In my research of more than 1,500 leaders at all levels of business and industry, an agile mindset is tightly linked to two key aspects of agility: Responsiveness and Resourcefulness.
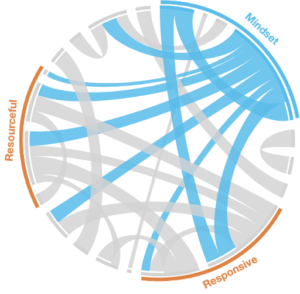
In particular, the ability to quickly turn challenges into opportunities and look for opportunities in the midst of change are strongly connected to Agility Shift Inventory-takers’ ability to be responsive and resourceful. These mindset attributes also strongly differentiate the most agile from the least agile respondents in the Agility Shift Inventory.
Reinforcing our research, when Nigel Davies at Forbes interviewed several leaders about the pitfalls of adopting agile, he also found that mindset was a common challenge.
For example, Christopher McFarlane, an agile project manager for Walmart Canada, shared with him, “instilling an agile mindset internally is one of the hardest things about the transition.” Successfully building an agile organization is also an endurance sport, says David Fort, managing director at Haines Watts Manchester, “Being an agile business isn’t a start-stop scenario, it’s a constant shift in culture and balance that has to be regularly revisited. If you stop running as an agile business, you’re likely to seize up. The real challenge is ensuring the agility is fresh, and the team members are focused on being agile.” (Davies, 2019)
Adding urgency to the need to attend to the leadership mindset is that many organizations are not yet seeing the expected returns of their formidable investments in agility because leaders underestimated the mindset and cultural shift that would be required for a successful transformation.
Mindset and culture are directly linked. Mindset influences thinking; thinking influences our actions; culture is created through repeated patterns of thinking and acting.
Version One’s survey of 1,319 leaders in organizations ranging from less than 1,000 employees to greater than 20,000 found that the top challenge in a successful agile transformation is that their current culture is at odds with the degree of communication, collaboration, self-organization and continuous learning that is at the heart of agile practices. Coming in a close second is an overarching organizational resistance to change (13th Annual State of Agile Report, 2018).
There is good news, however. The Forbes Insights and the Scrum Alliance report cited earlier also found that those organizations that were realizing results from their adoption of agile practices also reported strong cultural alignment, while those that were not yet seeing a return cited organizational culture as the impediment (2018). Leaders have a significant influence over the success or failure of agile initiatives as they set the tone, model, and reinforce the underlying beliefs, values, and behaviors that make up their organizational cultures.
This growing body of evidence all points in the same direction: any organization that makes agility a top strategic priority, must also prioritize learning and talent development strategies that support the critical mindset and behavioral shifts necessary to achieve the results of these investments.
Our work in recent years with companies like T-Mobile (see case story and webinar) demonstrates the power of engaging leaders across the enterprise in high-content, high engagement learning, and development experiences and has yielded exciting results. In addition to high net-promoter scores, showing initial enthusiasm, a rigorous analysis of how learning is being applied across the organization is demonstrating significant business value. If an organization like T-Mobile, operating in an extremely competitive environment and through years-long uncertainty of a possible merger can sustain results, your organization can, too.
Supporting Your Organization’s Agility Shift Through Learning and Talent Development
Just like reaching your health and fitness goals, developing and sustaining business agility, is not a one-time endeavor but a commitment to a new way of life. Fitness experts have found that the secret to sustained success is consistency and variety. The same is true for your organization’s leadership, team, and organizational agility.
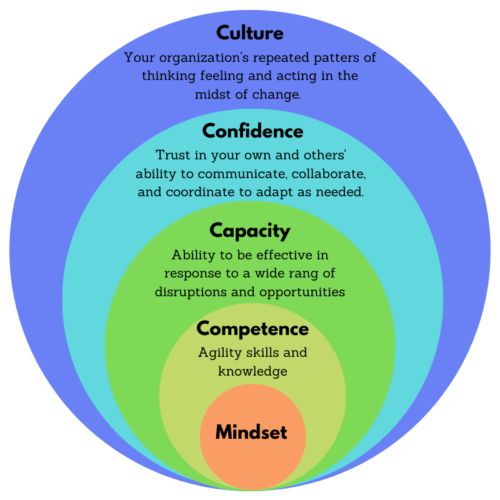
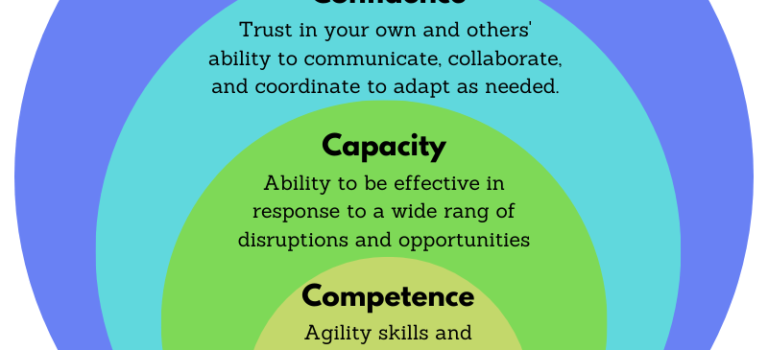
Making the Agility Shift
Attaining a consistent practice for agility requires an approach that includes enough variety to keep your workforce stretching and growing. The strategies we have found most impactful put the mindset shift in the center and build the Three Cs of The Agility Shift: Competence, Capacity, and Confidence. Consistent and innovative learning and development approaches in each of these areas reinforce a culture in which agile thinking and behavior can thrive.
Scalable Talent Development Approaches for Agile Leaders, Teams, and Organizations
One of the challenges in supporting organization-wide agility initiatives is providing meaningful and impactful learning opportunities across the enterprise. Whether led by your in-house training team or outside contractors, you are likely constrained by budget, available time (both training professionals’ and employees’ available time), as well as personnel.
We use several highly adaptable strategies to help our clients overcome these barriers:
- Human Resource Strategies: To ensure an integrated approach across the organization, we often work with HR and Talent Development leaders. Aligning staffing, talent development, performance appraisal, and coaching with agile organizational goals helps assure that you are building a workplace culture in which agility can thrive.
- Train-the-Trainer: We work with in-house learning and development professionals to train and certify them in customizable modules that they can then use to lead sessions for leaders at all levels of the organization. We provide an Agility Shift Facilitator Guide and participant materials. This approach offers the most flexible and comprehensive approach for building and sustaining an agile workforce.
- Agility Champion Training: In this immersive training session, we help designated Agility Champions throughout the organization learn the foundational concepts and best practices of team and leadership agility, while building their competence, capacity and confidence as an agility resource person, coach and activity facilitator. Agility Champions are also trained on and given access to a series of micro-learning resources and Take it to Your Team activities they can use to support continuous leadership and team development.
- Agility Lab Micro-learning Resources: Many managers and agile team leaders like to integrate our range of micro-learning resources and guided activities to support team engagement, innovation, and performance. These resources can be used one-on-one or to kick-off a meeting, planning session or integrated into a retrospective.
- Agility Assessment: Often, the biggest challenge in making the Agility Shift is the mindset shift and understanding how that mindset shift translates into new habits in each of the six dynamics of the agility shift. The Agility Shift Inventory (ASI) helps individuals and teams discover where their greatest strengths and opportunities lie and so that they invest their time and resources for maximum impact.
- Coaching: Because agile ways of thinking and working represent a significant shift for most leaders and team members, we provide individualized coaching to help contributors make their own agility shift so they can ensure their teams and the organization realize results from their agile initiatives.
- Leadership Development: An agile leader is anyone who spots a challenge or opportunity and effectively responds. Now more than ever, organizations need agile leaders at all levels of the business who can lead effectively in the midst of rapid change and uncertainty. Your current and emerging leaders need to be able to consistently model and inspire others to make the Agility Shift.
- Team Development: Agile organizations are team-centric and increasingly networked. The best investment you can make is in team success, whether or not you are adopting agile methodologies, teams need to be able to effectively innovate and adapt, as well as communicate, collaborate and coordinate resources. We help teams build their agility competence through high-content, high-engagement development days that integrate reflection and action planning based on the results of their Team Agility Shift Inventory.
- Customized Solutions: There is no one-size-fits-all solution for any organization. Your business priorities, leadership commitment, environment, and available resources all dictate which strategy is best for you. We work with organizations to determine the approach that will be most effective and sustainable to improve performance.
When You Should Consider an Agile Learning and Talent Development Approach
The good news is that building your organization’s overall competence, capacity, and confidence in agility is compatible with overall organizational agility objectives and each of the agile methodologies and agile transformation approaches described in this blog series. Not only is it compatible, but it is essential that you provide engaging and motivating development opportunities and help your leaders and teams make and sustain the necessary mindset and practical shift required to deliver results. Because we, as humans, are hard-wired to scan our environments for threats (read changes and disruptions) and avoid or resist them at all costs, we need new and continuous practices to help us make the intentional shifts to help us maximize each new disruption and opportunity. Whichever approach you choose, you need to have a strategy that helps your human system of interactions engage with and deliver the positive benefits and outcomes of your agility shift.
Which learning and development approach is right for you?
SCHEDULE TIME WITH PAMELA MEYER TO FIND OUT
Pamela Meyer, Ph.D. is the author of The Agility Shift: Creating Agile and Effective Leaders, Teams and Organizations. She is a sought-after keynote speaker and works with leaders and teams across industries who need innovative learning and talent development strategies to make the mindset and business shift to compete in a rapidly changing marketplace.
Additional References
13th Annual State of Agile Report. (2018). Retrieved from https://www.stateofagile.com/
Davies, N. (2019). Agile Deserves The Hype, But It Can Also Fail: How To Avoid The Pitfalls. Forbes. Retrieved from Forbes website: https://www.forbes.com/sites/nigeldavies/2019/07/02/agile-deserves-the-hype-but-it-can-also-fail-how-to-avoid-the-pitfalls/#c9ced757a0cf
How Agile and DevOps enable digital readiness and transformation. (2018). Hampshire, UK: Freeform Dynamics.
The Elusive Agile Enterprise: How the Right Leadership Mindset, Workforce and Culture Can Transform Your Organization. Jersey City, NJ: Forbes Insights and the Scrum Alliance (2018). Retrieved from: https://www.scrumalliance.org/ScrumRedesignDEVSite/media/Forbes-Media/ScrumAlliance_REPORT_FINAL-WEB.pdf
Schwartz, J., Collins, L., Stockton, H., Wagner, D., & Walsh, B. (2017). Rewriting the Rules for the Digital Age: 2017 Deloitte Human Capital Trends. Retrieved from: https://www2.deloitte.com/content/dam/Deloitte/global/Documents/HumanCapital/hc-2017-global-human-capital-trends-gx.pdf


 enterprise develop their learning agility competence, capacity, and confidence.
enterprise develop their learning agility competence, capacity, and confidence.

 Written by
Written by 
 employee development be shared across organizational roles, especially by the employees themselves. This means helping employees become more learning agile. Just as healthy people don’t abdicate responsibility for their wellness because they have access to doctors, we don’t want our employees to give up responsibility for their learning and growth because the company offers training resources.
employee development be shared across organizational roles, especially by the employees themselves. This means helping employees become more learning agile. Just as healthy people don’t abdicate responsibility for their wellness because they have access to doctors, we don’t want our employees to give up responsibility for their learning and growth because the company offers training resources.




 Does your organization have access to a diverse network of skills, knowledge, talent, and resources to respond to opportunities and challenges as they arise?
Does your organization have access to a diverse network of skills, knowledge, talent, and resources to respond to opportunities and challenges as they arise?
 By using the fitness metaphor, we can move beyond purely metric-based approaches to balance, such as Balanced Scorecard, the strategic and performance management system, and inspire fresh thinking and practices.
By using the fitness metaphor, we can move beyond purely metric-based approaches to balance, such as Balanced Scorecard, the strategic and performance management system, and inspire fresh thinking and practices.  One of the most effective ways to ensure the capacity to make those adjustments while making forward progress is to weave a robust
One of the most effective ways to ensure the capacity to make those adjustments while making forward progress is to weave a robust 

 book,
book,  indulgent time of year.
indulgent time of year. need to do is think of a time when you let your own health and well-being practices slip. Perhaps you were in a stressful period of work, or recent travels disrupted your exercise routine and healthy eating habits.
need to do is think of a time when you let your own health and well-being practices slip. Perhaps you were in a stressful period of work, or recent travels disrupted your exercise routine and healthy eating habits. 
 your core strengths can quickly lead to organizational instability.
your core strengths can quickly lead to organizational instability.
 is a new opportunity to strengthen and engage your Relational Web and you should take it!
is a new opportunity to strengthen and engage your Relational Web and you should take it! building your relationships. Do you have some gaps in your Relational Web that need filling in? Maybe you are looking for an executive coach to recommend to a client or additional marketing resources. Remember,
building your relationships. Do you have some gaps in your Relational Web that need filling in? Maybe you are looking for an executive coach to recommend to a client or additional marketing resources. Remember,  Talking about what you enjoy is often contagious and will open up the conversation. Some of my favorite non-work topics are skiing (though be careful of showing too much interest!), recent travel adventures and the latest developments in arts and culture. Be sure your enthusiasm doesn’t hi-jack the conversation. Share just enough to give others a chance to share theirs.
Talking about what you enjoy is often contagious and will open up the conversation. Some of my favorite non-work topics are skiing (though be careful of showing too much interest!), recent travel adventures and the latest developments in arts and culture. Be sure your enthusiasm doesn’t hi-jack the conversation. Share just enough to give others a chance to share theirs.

 green and red distractions on every corner?
green and red distractions on every corner? 

