By Pamela Meyer, PhD with contributions from Nick Freiling, Director of PeopleFish
Since launching the Agility Shift Inventory(TM) we have collected and analyzed thousands of inventories (ASI) from people working in organizations large and small across industries and nations. Each individual who takes the ASI receives a snapshot of their current agility capacity and opportunities based on their answers. They also receive our complimentary Agility Shift Catalyst and Conversation Guide, which provides a series of reflective questions and action steps to help them begin to make their own individual agility shift.
While individuals are using their results to expand their own agility, competence, capacity, and confidence, we have been aggregating and analyzing the anonymized results looking for additional trends and actionable insights to help our clients reach their business goals.
Our Surprising/Not so Surprising Finding
One of the first things that caught our attention was how significant an individual’s Relational Web plays as a predictor of their overall agility. If you are new to the six dynamics of The Agility Shift, the Relational Web is your web of skills, knowledge, talent, and resources that you need to be able to tap at a moment’s notice when things don’t go as planned or when a new opportunity emerges.
Understanding the Dynamics of Your Relational Web
The Relational Web is woven into the other five dynamics of agility and is at the center of the Agility Shift model for a reason. All of my prior research and experience helping organizations become more agile and innovative showed a link between the size and diversity of the Relational Web to individuals, teams, and the entire organization’s ability to be agile.
We were surprised and excited by additional correlations we found between an individual’s Relational Web and other agility-enhancing behaviors. For example, those who report intentionally making and building connections that expand their Relational Web are also significantly more likely to practice other key behaviors linked to overall agility. These include evaluating the diversity of relationships to ensure access to multiple perspectives, effectively making sense and meaning of what is happening when things don’t go as planned, and intentionally becoming aware of new resources in the environment.
The graphic below highlights some of the most interesting and actionable correlations.

These findings align with other recent research, such as the Google study of 180 of their teams, in which they found that the most successful teams had leaders with the largest and most diverse social networks (one aspect of the Relational Web). These leaders were also intentional about making and building their connections by doing things like regularly rotating who they ate lunch with.
We have long known of the importance of networking for career success. Our latest findings highlight the value of consistently and intentionally weaving a dynamic Relational Web for sustained agility.
So What? Turning Insight into Action
Whether you are a sole practitioner, individual contributor, or a leader with hundreds of reports, there are things you can do to turn these latest insights into positive action:
Expand your awareness and access to available resources. Attend (or organize) meet and greets for new colleagues. Learn about emerging technologies or other relevant developments in your environment.
Build meaningful connections with other people. This goes beyond sending and accepting LinkedIn invites. It means understanding the value of building connections founded on more than their transactional or operational value.
Participate in informal networks and affinity groups. Whether in a focused Community of Practice or simply a community, you can connect and build relationships and share resources with others who share your passion for continuous growth and learning.
Review your onboarding experience with the RW in mind—does it help people discover who does what, become familiar with available resources, and build relationships?
Seek and provide opportunities to expand your/your employees’ Relational Web and organize/participate in:
- Volunteer projects
- Job shadowing/mentoring programs
- Recreational activities
- Off-sites
- Industry, vendor, or practice-area conferences
- Lunch & Learns
To assess the current state of your Relational Web and other agility capabilities, I invite you to take the complimentary Agility Shift Inventory.
We have also developed a Team version of the ASI designed to give your entire team or department actionable insights for building on their strengths to improve agility and overall business results. Our clients find this resource particularly valuable to jumpstart agility or to help their team lay the foundation for success, whether they are adopting agile project management methodology or simply wanting to improve overall success.
Contact us here for more leadership agility development strategies



 Are you and your workforce able to move quickly with the needs of the market?
Are you and your workforce able to move quickly with the needs of the market?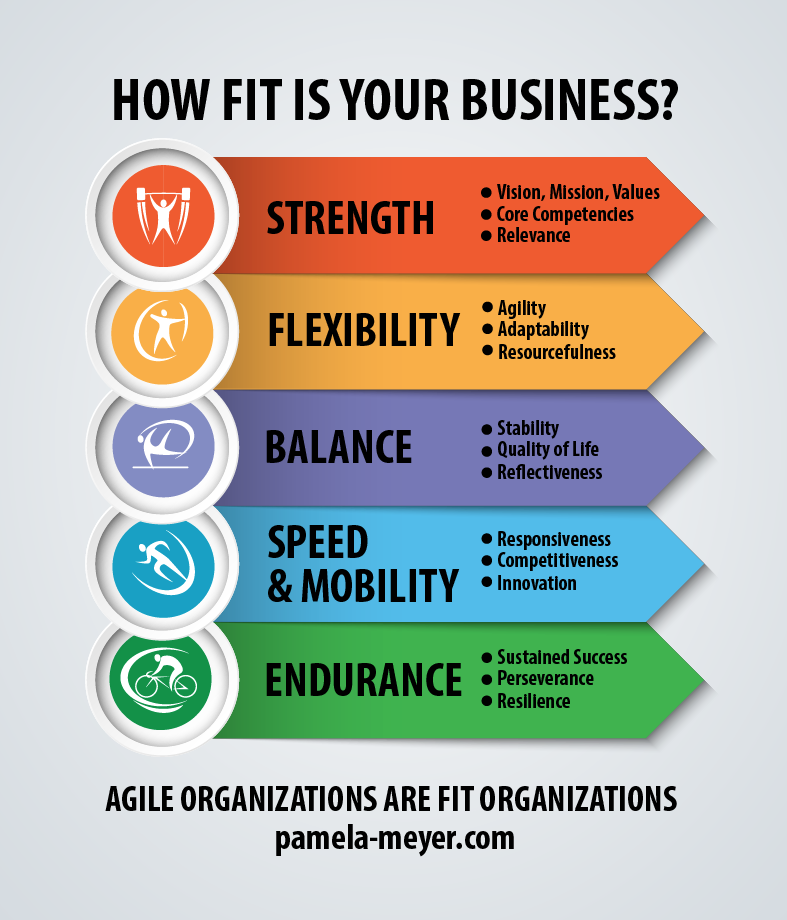 need. Similarly, your workforce is ready when it can rapidly mobilize to respond to a new opportunity, a shift in the market, or even a crisis.
need. Similarly, your workforce is ready when it can rapidly mobilize to respond to a new opportunity, a shift in the market, or even a crisis.

 Have you developed the competence and capacity to adapt when things don’t go as planned?
Have you developed the competence and capacity to adapt when things don’t go as planned? One of the best ways to improve collaboration and flexibility only takes a few minutes. Try it the next time you meet with your team. Kick off your meeting with a quick
One of the best ways to improve collaboration and flexibility only takes a few minutes. Try it the next time you meet with your team. Kick off your meeting with a quick


 The good news is that for those that develop this sense of urgency, the success rate may be as high as 75% (Kotter, 2006). As you look ahead to all you want to create and accomplish in the new year, take time to engage your colleagues’ hearts and minds in the urgent need to develop organization-wide competence, capacity and confidence to execute your strategy with agility.
The good news is that for those that develop this sense of urgency, the success rate may be as high as 75% (Kotter, 2006). As you look ahead to all you want to create and accomplish in the new year, take time to engage your colleagues’ hearts and minds in the urgent need to develop organization-wide competence, capacity and confidence to execute your strategy with agility.