
After a busy fall helping leaders become more agile in organizations here and abroad, I am waxing my skis and getting ready to head to ski racing camp in Colorado later this week.
This will be my fifth year in a row. I blocked the dates and sent in my deposit as soon as camp was announced—not because it is comfortable or even fun, at times it is, but the real reason I started going and continue go is that it scares me.
Followers of my sporadic blog posts know that I returned to ski racing, a somewhat delusional passion from my Iowa youth (I seriously thought I could be a contender!), after a birthday that ended in “0”. I skied every chance I could as a teenager—park district bus trip to Wisconsin (I’m on it!), University of Iowa ski trip to Colorado that they foolishly opened up to area high school kids (I’m in!), weekend trips with my parents to Midwest resorts and the occasional Colorado ski vacation (I planned the rest of my life around them!).
The Racing Bug
Somewhere along the way, I got bit by the racing bug and also started racing in as many USSA Central division races as I could get to, which included road trips to Minneapolis to race at Buck Hill, long before Lindsay Vonn, who got her start there, was born!
Coming back to skiing and ski racing when most of my friends have long since hung up their long underwear has taken a lot more commitment. When I was younger, it was easy to round up a group of adventurers willing to give it a go—many clad in their Iowa overalls.

The Author, Pamela Meyer
These days, it is much harder for me to find friends who want to head down the hill on two waxed planks, let alone into the cold. It was this challenge that led me to explore more organized ski activities, including racing clubs and camps.
With a great recommendation from a friend and former ski instructor, I found my way to Dave Gregory’s Peak Performance Ski Camp that he holds each November at Copper Mountain and summers at Mount Hood, Oregon.
Now, as I pack up for my fifth trip, I have a little better idea of what to expect, and yet, the apprehension has not completely lifted. Did I train well enough? You can never be too fit for racing. Will I crash? No question. Will I get hurt? It’s happened and is always a possibility. I still go because it still stretches me. It still scares me—not in a “why again am I jumping out of this airplane?” way—but in a way that pushes me out of my comfort zone, physically, socially, mentally.
Accepting the Challenge
Some years it takes, even more, commitment and intentionality. Two years ago, I had major surgery over the summer and had to make a concerted effort to recover, rebuild my strength and confidence. Last year, I fractured my shoulder on a training run. These experiences don’t deter me or my fellow masters racers. They do give me even greater respect for athletes such as Lindsay Vonn who had countless setbacks in their careers and yet came back, again and again. They make the effort and put in the work to return to peak performance, even when they have every invitation to use the latest injury to make a graceful exit from the competition (which Vonn, of course, did this past season).
My experience in life and especially these last few years, helping leaders, teams and organizations become more agile is that doing what scares you is where the learning is.
New learning, and especially the confidence to apply that learning under pressure, doesn’t happen by staying in our comfort zone. It doesn’t happen if you are afraid of looking silly, incompetent and like we don’t know what we are doing. As uncomfortable as these experiences are, they are the hallmarks that learning (or at least the potential for learning) is happening. Agile leaders not only seek out new experiences that stretch their current skills and abilities, but they also model their learning and share the process of becoming more confident with others. This, admittedly, takes some courage and a certain amount of psychological safety. In fact, it took me some time to muster this courage the first year I registered for racing camp.
Becoming Comfortable Being Uncomfortable

The biggest lesson I have learned as I pack up for camp #5 is that being a little (and sometimes a lot) out of my comfort zone is where the growth and where new confidence is built. One of our race coaches says, “If you never crash, you aren’t trying something new. You aren’t learning!”
I realized I can’t very well travel the world talking about The Agility Shift and helping leaders be more effective in the midst of the unknown if I am not challenging myself to do the same. And leaders at all levels of the organization cannot very well ask others to take risks and continue stretching, growing and adapting to changes if they are not willing to do so themselves.
So, as we move into the holiday season, which is often associated with cocooning, being cozy with friends and family (which is a wonderful way to recharge our spirits), I invite you to also look for the opportunities that lie ahead that scare you. It doesn’t have to be ski racing or even a physical challenge. Maybe it is just accepting an unexpected invitation before you start over-thinking it, go ahead and say, “yes!” sign up, and jump in. Maybe I’ll see you there!
What are you doing/might you do that scares you?
•••••
NOTE: This post is a revision of a 2017 post, updated with gratitude to be healthy and able to get out there for another season.

 Written by
Written by 
 employee development be shared across organizational roles, especially by the employees. This means helping employees become more learning agile. Just as healthy people don’t abdicate responsibility for their wellness because they have access to doctors, we don’t want our employees to give up responsibility for their learning and growth because the company offers training resources.
employee development be shared across organizational roles, especially by the employees. This means helping employees become more learning agile. Just as healthy people don’t abdicate responsibility for their wellness because they have access to doctors, we don’t want our employees to give up responsibility for their learning and growth because the company offers training resources.




 Are you and your workforce able to move quickly with the needs of the market?
Are you and your workforce able to move quickly with the needs of the market?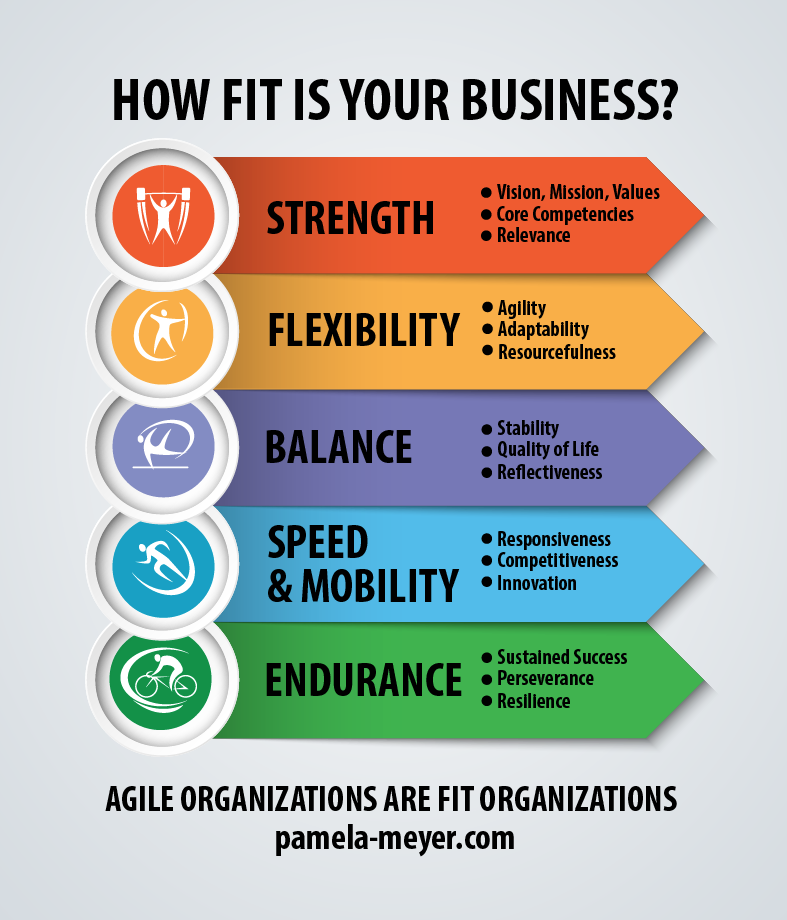 need. Similarly, your workforce is ready when it can rapidly mobilize to respond to a new opportunity, a shift in the market, or even a crisis.
need. Similarly, your workforce is ready when it can rapidly mobilize to respond to a new opportunity, a shift in the market, or even a crisis.

 Have you developed the competence and capacity to adapt when things don’t go as planned?
Have you developed the competence and capacity to adapt when things don’t go as planned? One of the best ways to improve collaboration and flexibility only takes a few minutes. Try it the next time you meet with your team. Kick off your meeting with a quick
One of the best ways to improve collaboration and flexibility only takes a few minutes. Try it the next time you meet with your team. Kick off your meeting with a quick